Minimally invasive cholecystectomy – advantages of laparoscopic and robotic approach
Minimally invasive surgery has revolutionized the treatment of gallbladder diseases. Today, cholecystectomy is performed primarily using the laparoscopic approach, considered the gold standard, but the option of robotic surgery is becoming increasingly common. Both techniques have their advantages and limitations – from shorter hospital stays and reduced pain to advanced 3D visualization and greater precision of instrument movements. This article explores the procedure, highlights the benefits of each method, and explains why the choice of technique depends not only on the patient but also on the team’s experience and equipment availability.
Cholecystectomy is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures, currently mostly using minimally invasive methods. This approach provides patients with many benefits such as shortened hospital stay, smaller wounds which decreases the chance of postoperative hernia development, decreased analgesics administration and comparable frequency of postoperative complications (according to classic approach). Laparoscopic approach is currently a golden standard of this surgery, therefore classic approach is only performer in complicated patients with previous abdominal surgeries in which adhesions and hard anatomical conditions are expected.
In the last 20 years robotic approach of cholecystectomy occurred. As researches show robotic cholecystectomy is comparably effective although it differs in some aspects and requires different equipment and medical staff. In this article we’re aiming to point the main differences, advantages and troubles associated with both methods of minimally invasive cholecystectomy.
Indications for surgery
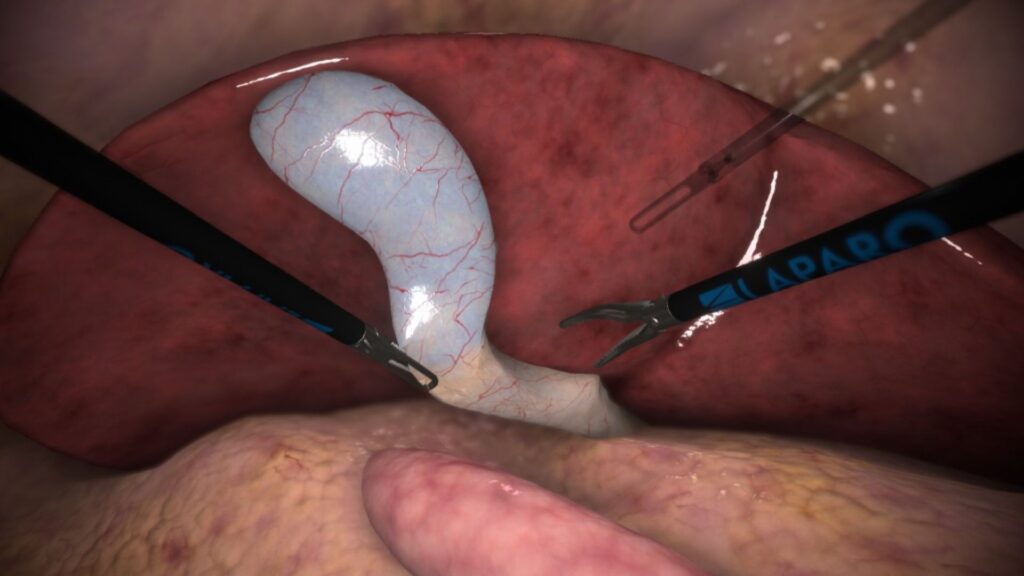
The most common indication for cholecystectomy is cholelithiasis manifesting with severe pain, jaundice and fever. Among rarer indications cholecystitis, gallbladder cancer and abscess can be distinguished. Gallbladder is localized on the inferior wall of the liver, near the liver hilum where the cystic duct joins the common hepatic duct to form the common biliary duct. Vascular support comes from the cystic artery which is the only vessel ligated during the procedure.
Course of the operation
Cholecystitis in both minimally invasive approaches is proceeded according to the same steps: dissection of Calots triangle and achieving the CVS – critical view of safety – which allows identification and propper ligation of biliary ducts. Next step is to dissect the cystic duct and cystic artery and close them using clips. Last step is cutting the mentioned structures, gallbladder dissection in order to uncouple it from liver and its removal using endobag.
Laparoscopic approach provides short operative time which decreases the time of anesthesia and therefore is safer for the patient, it is also way cheaper than robotic approach with comparable frequency of postoperative complications. Laparoscopic approach is widely known and practiced in medical centers so most of the surgeons archieved proficiency in performing it.
Robotic surgery
Robotic approach according to the recent research is associated with lesser frequency of bile duct injury, is as safe as laparoscopy but requires longer anesthesia time because of robot docking and undocking procedure. Performing the surgery on the robots console ensures surgeons comfortable and ergonomic position during the surgery and wrist-like mobility of robotic tools enables easier maneuvering in the surgical field. Additional advantage of robotic approach is stable vision and 3D visualization which eases identification of variable anatomy of this region. Picture quality is also higher in robotic compared to laparoscopic approach. Because of the fact that cholecystectomy is fairly easy and well known procedurę SAGES suggests to perform it on the robot as a bridge to more complex surgeries allowing surgeons training the proficiency in using the robotis system. It’s worth mentioning that robot requires more medical stuff to be trained in using it including nurses and technicians which prolongs the learning curve and the moment of achieving proficiency in using it.
Each of the approaches has a Single Site Surgery variant with all tools and camera inserted into one trocar, but outside of aesthetic values (one wound instead of few) this method causes limited mobility and makes dissection more troublesome.
Summary
Summing up, there’s no obvious statement which of the minimally invasive approaches is better, choice should be dependant of staff preparation, economical aspects, tools availability and patients anatomical conditions. Both methods have their advantages above the other and both provide patient with safety and good medical outcomes. Nowadays laparoscopic approach is much more widely used because of its common availability although robotic approach also appears on the surgical wards.
Author: Adam Hajdaniak

